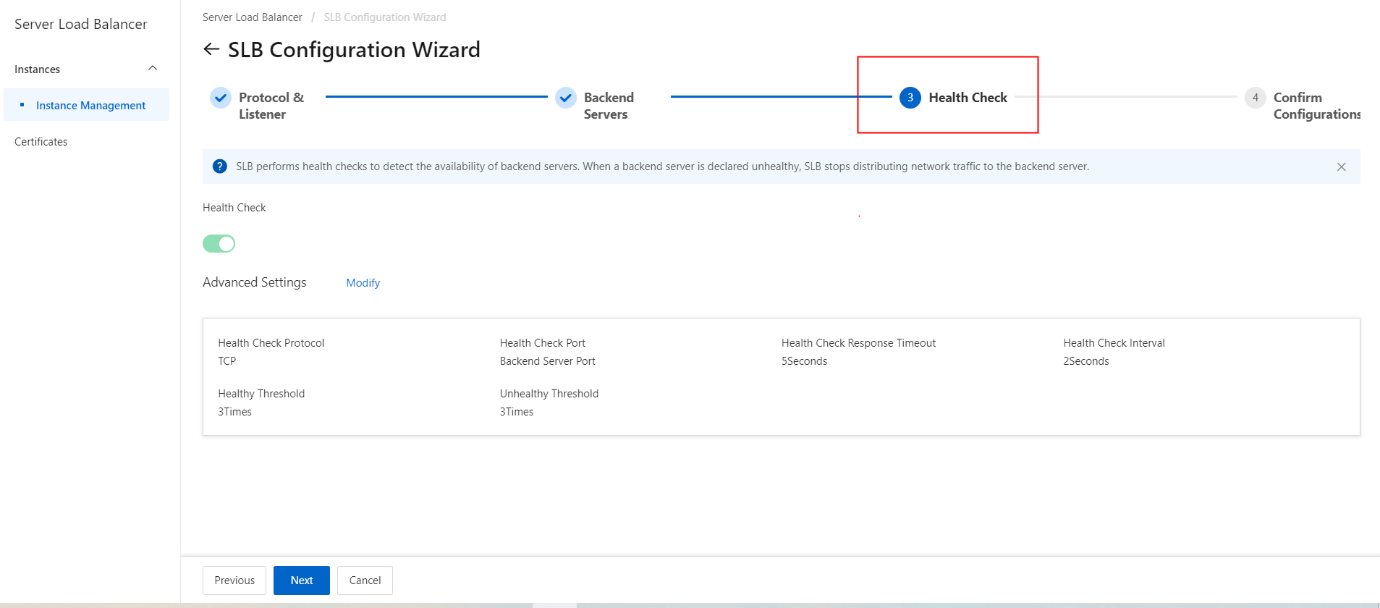
Configure health checks
Procedure
This topic describes how to configure health checks. You can configure health checks when you add a listener. The default health check settings can meet your requirements in most cases.
Procedure
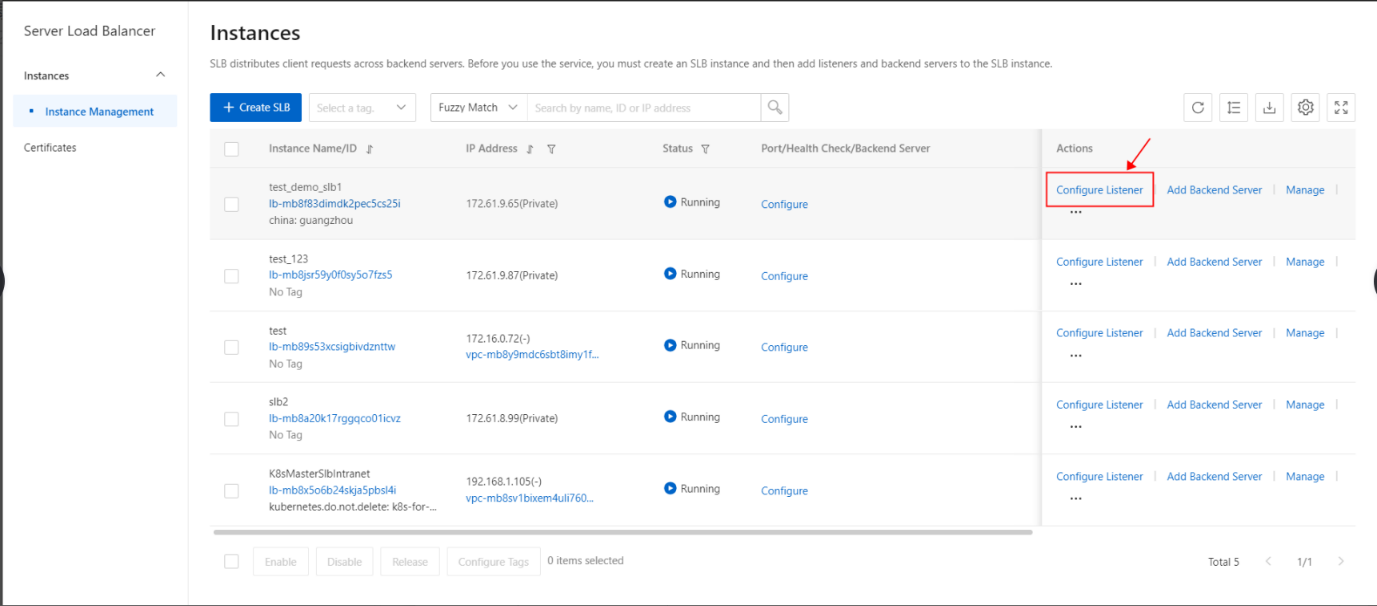
- On the SLB management console page, select the SLB instance to be operated, click Configure Listener or click to enter the SLB instance, and on the monitoring page, click Add listener.
- Click Next to go to the Health Check step and configure the health check. We recommend that you use the default settings when you configure health checks.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Health Check Protocol | Select the protocol that the SLB instance uses when it performs health checks. For TCP listeners, both TCP health checks and HTTP health checks are supported. · A TCP health check implements detection at the network layer by sending SYN packets to check whether a port is open. · An HTTP health check verifies the health of a backend server by sending HEAD or GET requests to simulate browser access. |
| Health Check Method (for the HTTP and HTTPS health checks only) | Health checks of Layer 7 (HTTP or HTTPS) listeners support both the HEAD and GET methods. The HEAD method is used by default. If your backend application server does not support the HEAD method or if the HEAD method is disabled, the health check may fail. To solve this issue, you can use the GET method instead. If the GET method is used and the response size exceeds 8 KB, the response is truncated. However, the health check result is not affected. Note Health checks of Layer 7 listeners of all regions support the GET method. |
| Health Check Path and Health Check Domain Name (Optional) (for the HTTP health checks only) | By default, SLB sends HTTP HEAD requests to the default homepage configured on the application server through the internal IP address of the backend ECS instance to perform health checks. If you do not use the default homepage of the application server for health checks, you must specify the path for health checks. Some application servers verify the host field in requests. In this case, the request header must contain the host field. If a domain name is configured in health check settings, SLB adds this domain name to the host field when SLB forwards a health check request to one of the preceding application servers. If no domain name is configured, SLB does not include the host field in requests and the requests are rejected by the application server, which may cause health checks to fail. If your application server verifies the host field in requests, you must configure a domain name in health check settings to ensure that the health check feature functions properly. |
| Normal Status Code (for the HTTP health checks only) | Select the HTTP status code that indicates successful health checks. Default values: http_2xx and http_3xx. |
| Health Check Port | The detection port used by the health check feature to access backend servers. By default, the backend port configured for the listener is used. Note If a VServer group or a primary/secondary server group is configured for the listener, and the ECS instances in the group use different ports, leave this parameter empty. SLB uses the backend port of each ECS instance to perform health checks. |
| Response Timeout | The length of time to wait for a health check response. If the backend ECS instance does not send an expected response within the specified period of time, the health check fails. Valid values: 1 to 300. Unit: seconds. Default value for UDP. listeners: 10. Default value for HTTP, HTTPS, and TCP listeners: 5. |
| Health Check Interval | The interval between two consecutive health checks. All nodes in the LVS cluster perform health checks independently and in parallel on backend ECS instances at the specified interval. The health check statistics of a single ECS instance cannot reflect the health check interval because the nodes perform health checks at different times. Valid values: 1 to 50. Unit: seconds. Default value for UDP. listeners: 5. Default value for HTTP, HTTPS, and TCP listeners: 2. |
| Unhealthy Threshold | The number of consecutive failed health checks that must occur on a backend ECS instance before this ECS instance is declared unhealthy. Valid values: 2 to 10. Default value: 3. |
| Healthy Threshold | The number of consecutive successful health checks that must occur on a backend ECS instance before this ECS instance is declared healthy. Valid values: 2 to 10. Default value: 3. |
| Health Check Requests and Health Check Results | When you configure health check for a UDP listener, you can enter the request content (such as youraccountID) in the Health Check Requests field and the expected response (such as slb123) in the Health Check Results field. This operation adds the health check response logic to backend servers. For example, slb123 is returned when a youraccountID request is received. If SLB receives the expected response from a backend server, the health check succeeds. Otherwise, the health check fails. You can use this method to improve health check accuracy. |